Graph Data Structure
A graph is a pictorial representation of a set of objects where some pairs of objects are connected by links. The interconnected objects are represented by points termed as vertices, and the link that connect the vertices are called edges. A graph is a pair of sets (V,E), where V is the set of vertices and E is the set of edges, connecting the pairs of vertices, looks the following.
V = {a, b, c, d, e} E = {ab, ac, bd, cd, ed}
Mathematical graphs can be represented in the data structure. We can represent a graph using an array of vertices and a 2D array of edges.
- Vertex: Each node of the graph is represented as a vertex.
- Edge: Edge represents a path between two vertices.
- Adjacency: Two node or vertices are adjacent if they are connected to each other through an edge.
- Path: represents a sequence of edges between the two vertices.
The operations are Add vertex, add edge, and display vertex.
The users of graph extends to almost every application in computer science including navigation systems, web page links, data transmission, social networks, fluid dynamics, critical path analysis, 3D modelling and game and simulations.
Typically a graph will have more edges than vertices, a graph with a lot of edges is called a dense graph, a graph with few edges in relative to vertices is called a sparse graph. In some graphs, a directed graph/digraph is when the edges are in one direction. A graph with bidirectional vertices is unordered graph or simply a graph. Each edge in the graph can have a weight associated to it. This is referred to as the cost/weight. A path is a sequence of vertices in the graph. A graph is said to be connected if there is a path between a vertex to each other vertex. A cycle is when the starting vertex is the same as the ending vertex. A tree is a special type of graph, where the starting is from the root node to every other node. But the tree has no cycles.
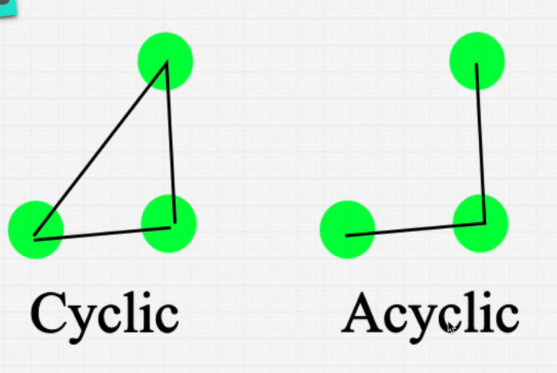
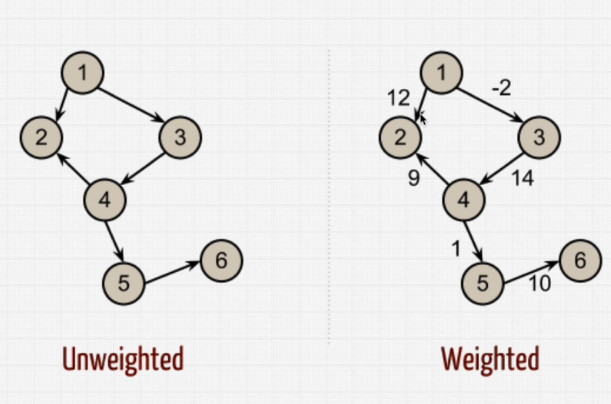

Therefore a graph can be classified into cyclic/acyclic - weighted/unweighted - direct/undirected.
Graph Implementation
An adjacent list: There is a master list of vertices. Each edge has a list maintaining the adjacent vertices. Very compact and space efficient. But to determine if a connection exist between two vertices then it will take time since you must go through each list and check. For a dense graph, the time will increase proportionally with the graph. An adjacent matrix: Every vertex is written as a row and heading. If the connection exists, it can be presented as a weight. Adjacent matrix is faster to than adjacent list when it comes to look up since it requires a simple array lookup. However, adjacent matrix is not efficient to space, for a sparse graph, much of the adjacent matrix it will empty. For a directed graph, half the information will be empty. What is traversing? Traversing is going through all or some elements of the data structure. Iteration is a type of traversal. visited
- Until the queue is empty