Tree data Structure
A tree presents the nodes connected by edges. Binary tree is a special data structure used for data storage purposes. A binary tree has a special condition that each node can have a maximum of two children. A binary tree has the benefits of both an ordered array and a linked list as search is as quick as in a sorted array and insertion or deletion operation are as in linked list.
A binary search tree is better than hash table in some cases because it preserves the relationship between your data.
Important Terms:
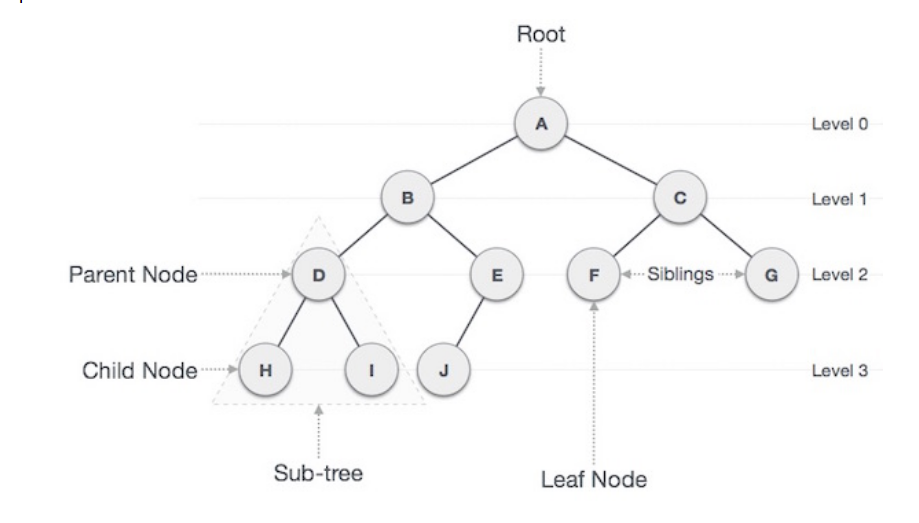
- Path refers to the sequence of nodes along the edges of a tree.
- Root is the node at the top of the tree. There is only one root per tree and one path from the root node to any node
- Parent: Any node except the root node has one edge upward to a node called parent
- Child: The node below a given node connected by its edge downward is called its child node
- Leaf: The node which does not have a any child node is called the leaf node
- Subtree represents the descendants of a node
- Visiting refers to checking the value of a node when control is on the node
- Traversing means passing through nodes in a specific order
- Levels: Level of a node represents the generation of a node.
- Key represents a value of a node based on which a search operation is to be carried out for a node.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Level 0: 2^0 = 1;
Level 1: 2^1 = 2;
Level 2: 2^2 = 4;
Level 3: 2^3 = 8;
# of nodes = 2^h - 1;
log nodes = height
In binary tree, we do not check every node. But we look at certain places due to how binary search tree are organized.
Binary Search Tree
A binary search tree exibiits a special behaviour where its node’s left child must have a value less than its parents value and the nodel right child must have a value greater than its parent value.
A Binary Search Tree is O(log n). To find the number of nodes in a perfect binary tree. We do the following:
A Binary Search Tree (BST) is a tree in which all the nodes follow the below-mentioned properties −
- The left sub-tree of a node has a key less than or equal to its parent node’s key.
- The right sub-tree of a node has a key greater than to its parent node’s key.
Thus, BST divides all its sub-trees into two segments; the left sub-tree and the right sub-tree and can be defined as −
1
left_subtree (keys) ≤ node (key) ≤ right_subtree (keys)
The BST operations are:
- Insert: Inserts an element in a tree/create a tree
- Search: Searches an element in a tree
- Preorder Traversal: Traverses a tree in a pre-order manner
- Inorder Traversal: Traverses a tree in an in-order manner
- Post order Traversal: Traverses a tree in a post-order manner
Insert operation
The insert operation works as follows
1) The very first insertion creates the tree 2) After that, whenever an element is to be inserted, first locate its proper location by searching from the root node 3) If the data is less than the key value, search for the empty location in the left subtree and insert the data. 4) Otherwise, search for the empty location in the right subtree and insert the data. Search operation: Whenever an element is to be searched, start searching from the root node, then if the data is less than the key vaue, search for the element in the left subtree. Otherwise, search for the element in the right subtree.
Tree Traversal
Traversing is the process of searching the nodes on a tree. We traverse a tree to search or locate a given item or key in the tree or print all the values it contains. There are three ways to traverse a tree
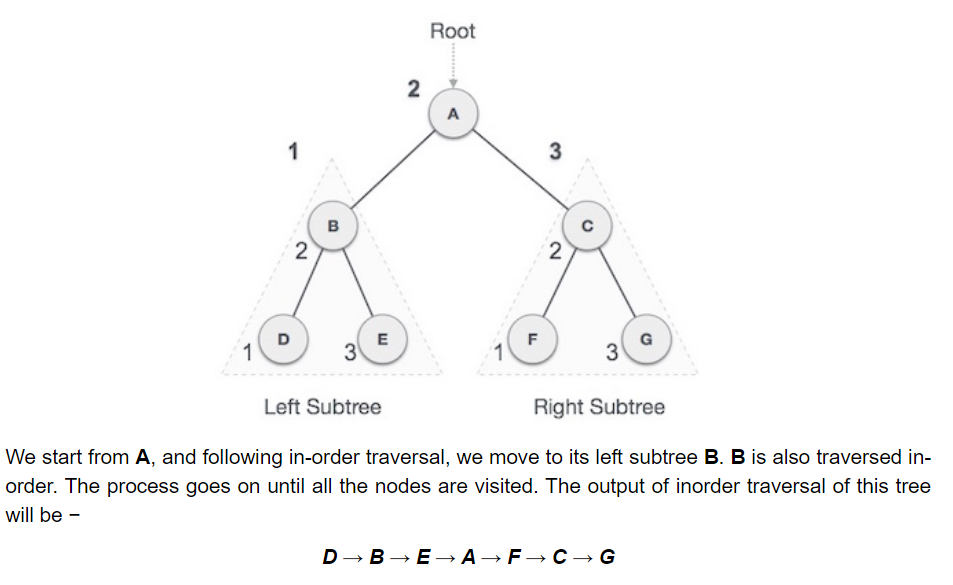
- In order traversal: As the name suggests, you take the leftmost subtree, then the next tree, in this case the root node, then the right subtree. In other words, the left subtree is visited first, then the root and later the right subtree. The output will produce sorted key values in an ascending order. D → B → E → A → F → C → G.
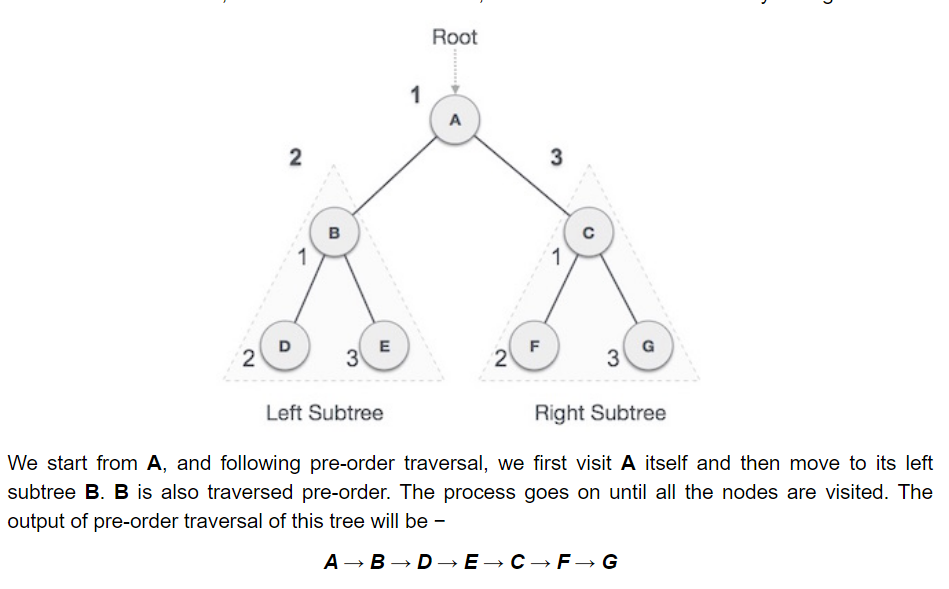
- Pre-order traversal: As the name suggests, you visit the root firstm then the left-subtree and its children, the right subtree and its children. In other words, The root node is visited first, then the left subtree and finally the right subtree. A → B → D → E → C → F → G.
- Post-order traversal: The leafs are visited first then the root of that (sub)tree. First, we traverse the left subtree, then the right subtree and finally the root node. It visits all the leafs before going into the root. D → E → B → F → G → C → A.
AVL (Adelson, Velski & Landis) Tree
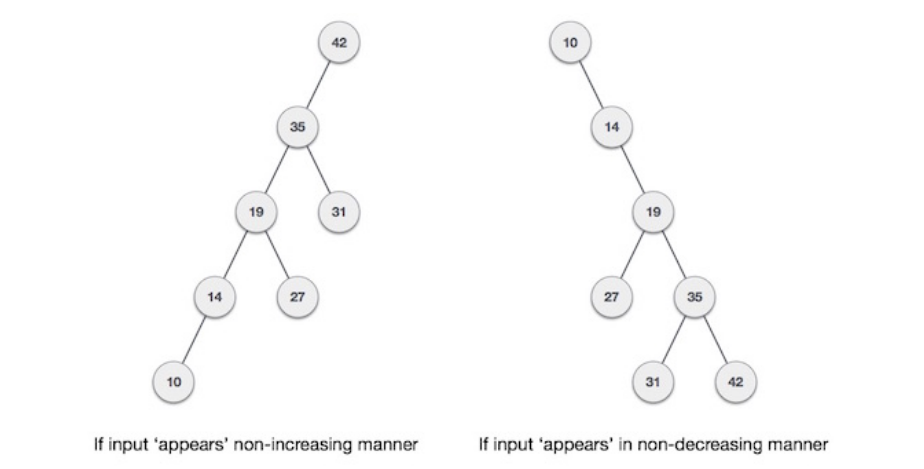
The goal is to always have a balanced binary tree since the worst-case scenario of a BST is closest to linear search algorithms, that is O(n). If the input comes in a non-increasing manner, or a non-decreasing manner as follows:
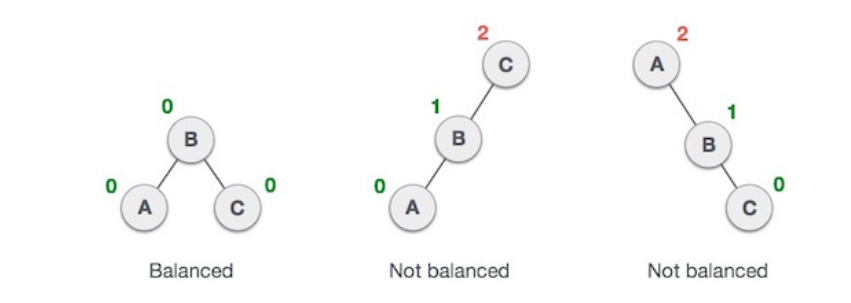
AVL is a height balancing tree where it checks the height of the left and right sub-tress and assures that the difference is not more than 1. This difference is called the balance factor. If the difference in the height of left and right subtree is more than 1, the tree is balanced using some rotation techniques.
To balane itself, there are 4 types of AVL rotations:
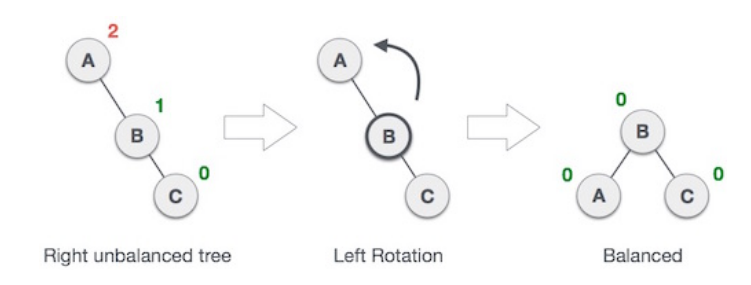
- Left Rotation: Single rotation
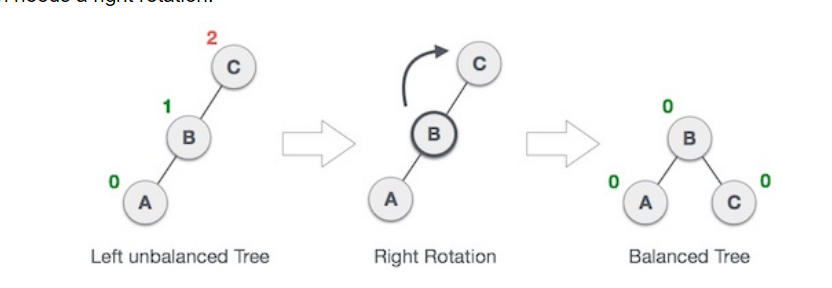
- Right Rotatin: Single rotation
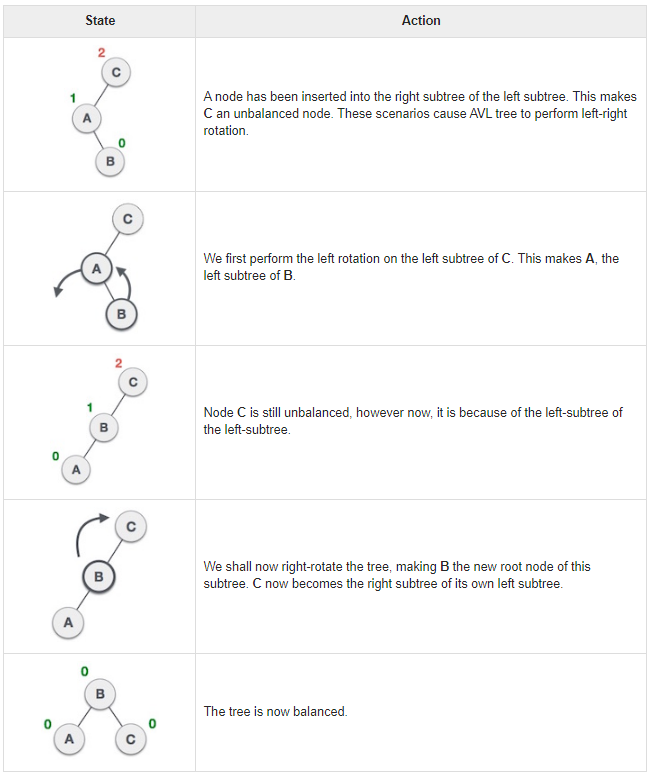
- Left-Right Rotation: Double rotation
- Right-Left Rotation: Double rotation
Left Rotation: Move the middle node and make it a root node, since it is the middle valye between A and C.
Right Rotation:Same method as above, by making the middle node, a root node, and converting the root node into leaf with the other leaf, then you get a balanced tree.
Left-right rotation: You do double rotations. A left-right rotation is a combination of left rotation followed by right rotation.
Right-Left Rotation: The second type of double rotation is Right-Left Rotation. It is a combination of right rotation followed by left rotation.
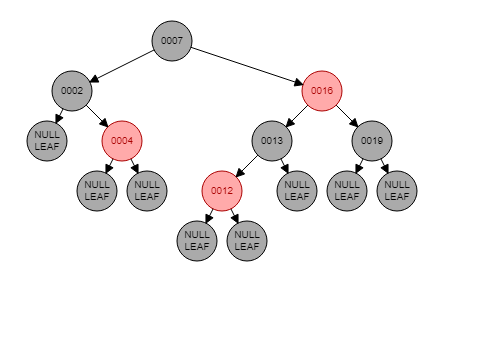
Red Black Tree
Red black tree is another method to deal with unbalanced binary trees. In a red black tree:
- A node is either red or black
- The root and leaves (NIL) are black
- If a node is red, then its children are black
- All paths from the a node to its NIL descendats contain the same number of black nodes
- Nodes require one storage bit to keep track of color
- Every path from a node (including root) to any of its descendant NULL node has the same number of black nodes.
- No red-red parent-child
The goal of rotation is to alter the structure of a tree by rearranging subtreees. In this way we decrease the height of the tree.
Red Black Trees are used in most of the language libraries like map, multimap, multiset in C++ whereas AVL trees are used in databases where faster retrievals are required.
- AVL trees are more rigidly balanced and hence provide faster look-ups. Thus for a look-up intensive task use an AVL tree.
- For an insert intensive tasks, use a Red-Black tree.
- AVL trees store the balance factor at each node. This takes O(N) extra space. However, if we know that the keys that will be inserted in the tree will always be greater than zero, we can use the sign bit of the keys to store the colour information of a red-black tree. Thus, in such cases red-black tree takes no extra space.
The AVL trees are more balanced compared to Red-Black Trees, but they may cause more rotations during insertion and deletion. So if your application involves many frequent insertions and deletions, then Red Black trees should be preferred. And if the insertions and deletions are less frequent and search is a more frequent operation, then AVL tree should be preferred over Red-Black Tree.
Check visualization here for practice https://www.cs.usfca.edu/~galles/visualization/RedBlack.html.
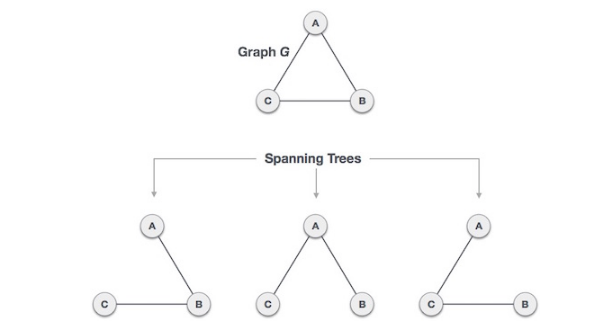
Spanning Tree
A spanning tree is a subset of graph G which has all the vertices covered with minimum possible number of edges. A spanning tree does not have cycles and cannot be disconnected. Every connected and undirected graph G has at least one spanning tree. A disconnected graph does not have any spanning tree, as it cannot be spanned to all its vertices. N^N-2 to get the number of spanning trees, where n is the number of nodes. Thus, we can conclude that the spanning trees are a subset of connected graph G and disconnected graphs do not have spanning tree. Also a single graph can have more than one spanning tree.
Properties of spanning tree:
- A connected graph G can have more than one spanning tree
- All possible spanning tree of graph G, have the same number of edges and vertices
- The spanning tree does not have any cycle (loops)
- Removing one edge from the spanning tree will make the graph disconnected. The spanning tree is minimally connected
- Adding one edge to the spanning tree will create a circuit or loop. i.e. The spanning tree is maximally acyclic.
A spanning tree is used to find the minimum path to connect all nodes in a graph. Common applications are:
- Civil Network Planning
- Computer Network Routing Protocol
- Cluster Analysis
Minimum Spanning Tree (MST): In a weighted graph, a minimum spanning tree is a spanning tree that has minimum weight than all other spanning trees of the same graph. Spanning tree examples are Kruskals algorithm and Prims algorithm which are examples of greedy algorithms.
Binary Heap
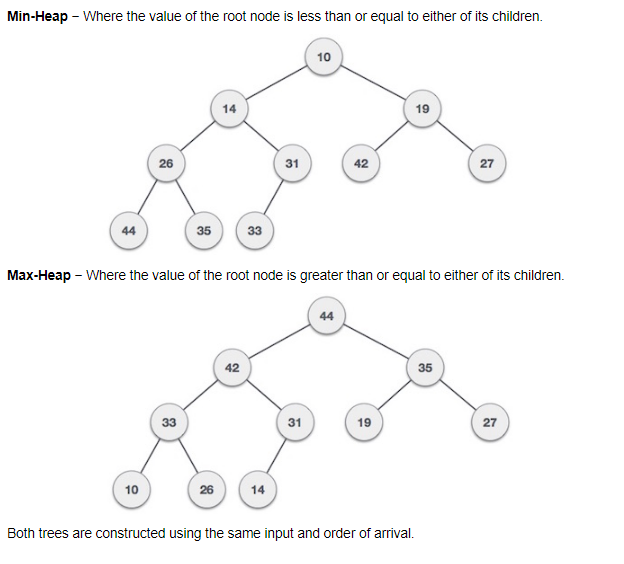
Heap: is a special case of a balanced binary tree data structure where the root-node key is compared with its children and arranged accordingly. There are two types of heap, the min-heap and the max-heap.
The min-heap is where the value of the root node is less than or equal to either of its children.
The max-heap is where the value of the root node is greater than or equal to either of its children. Best demonstrated with a diagram.
Binary heap is good for getting values larger or lower than a certain value. Binary heap are best when designing priority queues.
There is no concept of balancing in a binary heap, since they always maintain a binary by organizing it in order. The binary heap always gives a gurantee that the parent is greater than the children. In a normal queue, the method is FIFO. In a priority queue with a binary heap, some elements have a higher priority than others. For example, treating the patients with the most severe symptoms. The only downside is when you have a high value coming at the end, then you have to bubble up the value by comparing it to each node in the tree
Trie
Trie is a specialized tree used for searching strings. The root node is empty. It can have multiple chidren and not just binary. Trie is also called prefix tree. It is useful for autocompletion and text completion.
Use https://visualgo.net/en to visualize any of the algorithms